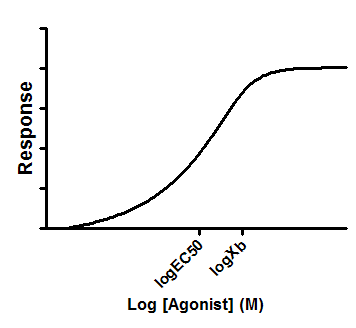
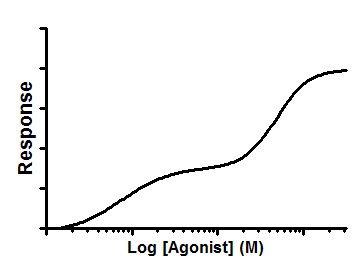
You can interpolate from any curve fit through a set of standards. However, the equations listed below are used most commonly. These equations are instantly available from the interpolation analysis. You'll also find this set of equations in the equation tree used in nonlinear regression.
Notes:
•These graphs show the curve going up (increasing Y) as X increases. But all will work for downward sloping curves too.
•All of these equations (except Pade) are also present in other equation folders in the nonlinear regression dialog.
Note that in nonlinear regression this equation is called "log(agonist) vs. response -- Variable slope" |
|
Note that in nonlinear regression this equation is called "[Agonist] vs. response -- Variable slope" |
|
Note that in nonlinear regression this equation is called "Asymmetrical (five parameter), X is log(concentration)" |
|
Note that in nonlinear regression this equation is called "Asymmetrical (five parameter). X is concentration" |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y=B0 + B1*X + B2*X^2 |
|
Y=B0 + B1*X + B2*X^2 + B3*X^3 |